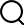How much do you know about composite current collectors?1. The concept of composite current collectorComposite current collector is a new type of current collector material composed of polymer material and metal, which mainly plays the role of collecting current and carrying positive and negative active materials. The composite current collector structure is similar to a "sandwich" structure, with a base film (PP, PET, PI and other polymer materials) in the middle, and copper-plated or aluminum metal films on the outer two layers.
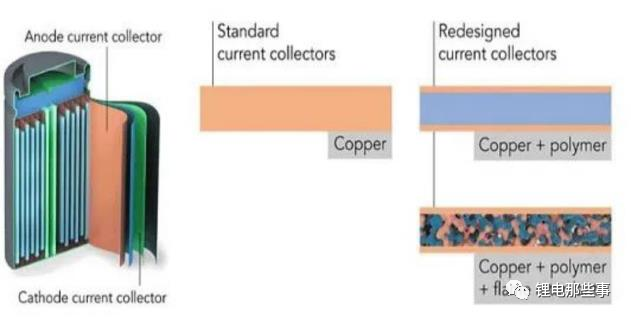
At present, the positive current collector is aluminum foil (MA), and the negative current collector is copper foil (MC). Copper, aluminum and other metals are widely used in lithium current collectors due to their high electrical conductivity, good electrochemical stability, and high mechanical strength. Among them, copper is relatively easy to oxidize at high potentials, and is mainly used for negative electrode current collectors. Aluminum is used as a negative electrode current collector for corrosion. It is more serious and is mainly used for positive current collectors.
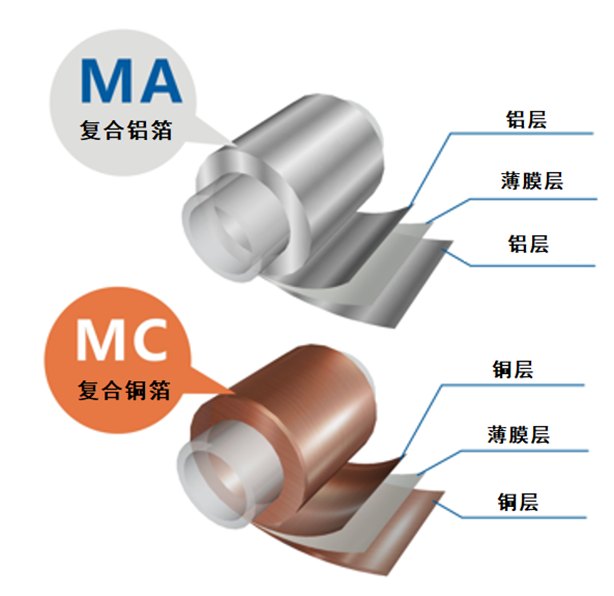
Composite copper foil (MC) intermediate base film is mainly made of PET, PP and other polymer materials, the thickness is generally 4-4.5μm, the double-sided copper plating layer is generally about 0.8-1.5μm, the total is 5.6-7.5μm, the conductivity can be ≤20mΩ.
The composite aluminum foil (MA) mainly adopts the vacuum coating process, first coats 8-15nm metal alumina through the evaporation kettle, and then thickens the aluminum layer by about 1μm. Considering the adhesion of aluminum ions, the composite aluminum foil base film is mainly made of PET material.
2. Advantages of composite current collectorsThe main advantages of composite current collectors lie in improving safety, increasing energy density, increasing service life and reducing raw material costs.
Good safety performance. The polymer substrate in the middle of the composite aluminum current collector has insulating and flame-retardant properties. Its metal conductive layer is thin, and it will blow like a fuse in a short circuit, and it will melt quickly before thermal runaway. The battery damage is limited to the puncture site to form a "point break". , Effectively form the "open circuit effect", prevent the battery from overheating due to continuous high current, effectively control the problem of battery thermal runaway, and improve battery life and safety.
High energy density. The middle layer of the composite current collector is made of lightweight polymer material, and its weight is 50%-80% lower than that of the pure metal current collector. As the proportion of weight decreases and the proportion of active materials in the battery increases, the energy density can be increased by 5%-10%. For 6μm copper foil, based on the calculation that the mass of copper foil accounts for 11% of the power battery, the use of PET, PP and PI polymer materials to replace part of the copper can increase the energy density of the power battery by 6.6%, 7.1% and 6.6%, respectively.
long life. The polymer material forms a layered annular sponge structure around the active material layer in the battery. During the charging and discharging process, the sponge structure can absorb the expansion-shrinkage stress caused by the insertion and extraction of lithium ions in the active material layer of the pole piece, and maintain the long-term integrity of the pole piece interface. Increase cycle life by 5%.
The cost advantage is obvious. From the perspective of raw material cost: PET/PP copper foil is about 34% of traditional copper foil; from the perspective of the total cost of finished products, it is estimated that PET copper foil will be about 70.8% of traditional copper foil in 2025, and PP copper foil will be about 70.8% of traditional copper foil. 79.6% of the foil.
3. Composite current collector process route selectionDifferent from the traditional copper foil production process, the process of composite copper foil is shortened, but the difficulty is greatly improved. The core of the technology is the metallization of the surface of the two-polymer material. The structure is represented by 4.5 micron PET and double-sided 1 micron. copper plating layer. The production methods currently used in the industry include one-step method (chemical deposition method/vacuum magnetron sputtering/vacuum evaporation method), two-step method (vacuum magnetron sputtering + water electroplating/vacuum magnetron sputtering + evaporation) and Three-step method (vacuum magnetron sputtering + vacuum evaporation + water electroplating).
One-step chemical deposition refers to the deposition of a copper layer by chemical reaction. First, the surface of the base film is cleaned and roughened to increase the surface roughness of the base film, and then the copper layer is deposited to form a good bonding force.
The vacuum magnetron sputtering and vacuum evaporation one-step method (One-step vacuum magnetron sputtering and vacuum evaporation) refers to depositing the copper plating layer to 1 micron by repeated magnetron sputtering or repeated evaporation. Vacuum evaporation is a dry coating method that does not use solutions or electrolytes to prepare thin films. It has the advantages of simple film formation method, easy operation, high film purity and compactness, and uniform film thickness. Compared with magnetron sputtering, the vapor deposition method has higher deposition efficiency for copper, which can greatly speed up the production cycle. However, the disadvantages of vacuum evaporation are also obvious. The method of heating and evaporation needs to be reversed in a high temperature environment, which is easy to cause damage to polymer materials and reduce the yield of composite copper foil.
4. Composite current collector base film selection
At present, there are three main research routes on composite copper foil base film materials in the market: PET, PP, and PI. The density of PET and PI is about 1/7 of that of copper, and the density of PP is 1/10 of that of copper.
PET has the best tensile strength, bending performance, high and low temperature resistance, insulation performance, etc., but its outstanding disadvantage is that it is not resistant to strong acid and alkali, and is easily corroded in the electrolyte environment, so the battery factory needs to adjust the electrolysis Liquid formula to improve.
PP has good acid resistance and can maintain good performance in a high-temperature electrolyte environment, but its toughness is insufficient, and it is easy to break during high-speed coating, which affects the overall yield. In addition, some composite current collector manufacturers have reported that PP material and copper layer The combination is less than expected.
PI materials have outstanding comprehensive advantages in terms of mechanical indicators, electrochemical properties, and high temperature resistance, but the production cost is too high to meet the industrial needs of reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
People in the industry generally believe that PET and PP composite technology are the first to be implemented, and PI is relatively lagging behind in the research and development stage due to high cost and difficult technical requirements. During the verification process, the PET route was basically rejected by the downstream. Due to the lithium alkoxide (the component of the SEI film) at the negative end of the lithium battery, it may promote the degradation of PET, resulting in the destruction of the entire current collector after the battery has been charged and discharged many times. Battery manufacturers are more inclined to PP (polypropylene) in terms of selection and layout. It is extremely difficult to undergo chain scission degradation and has strong chemical stability. It is currently the best choice.
Hangzhou Dahua Industry Control Technology Co., Ltd
. offer composite coppe foil slitting machine/composite aluminum foil slitting machine